Shoebox street light type 3 glass lens optical design
Original price was: $1,600.00.$1,380.00Current price is: $1,380.00.
Led glass lens is an optical element used for LED light sources. It focuses, diverges or evenly distributes the light emitted by LED through special design and materials, thereby improving the efficiency and effect of the light source. Its main features include:
1. Optical performance: Glass lenses can effectively control the direction and intensity of light and improve lighting effects.
2. Durability: Compared with plastic lenses, glass materials have better temperature resistance and wear resistance, and are not easily deformed.
3. Low light loss: High-quality glass lenses can reduce light reflection and absorption, maximizing the use of light emitted by LEDs.
4. Diversity: Can be designed into different shapes and curvatures according to different lighting needs, such as spherical lenses, aspheric lenses, etc. Application areas include but are not limited to indoor lighting, outdoor lighting, automotive lighting, etc. By properly configuring LEDs and glass lenses, lighting quality and effects can be significantly improved.
Description
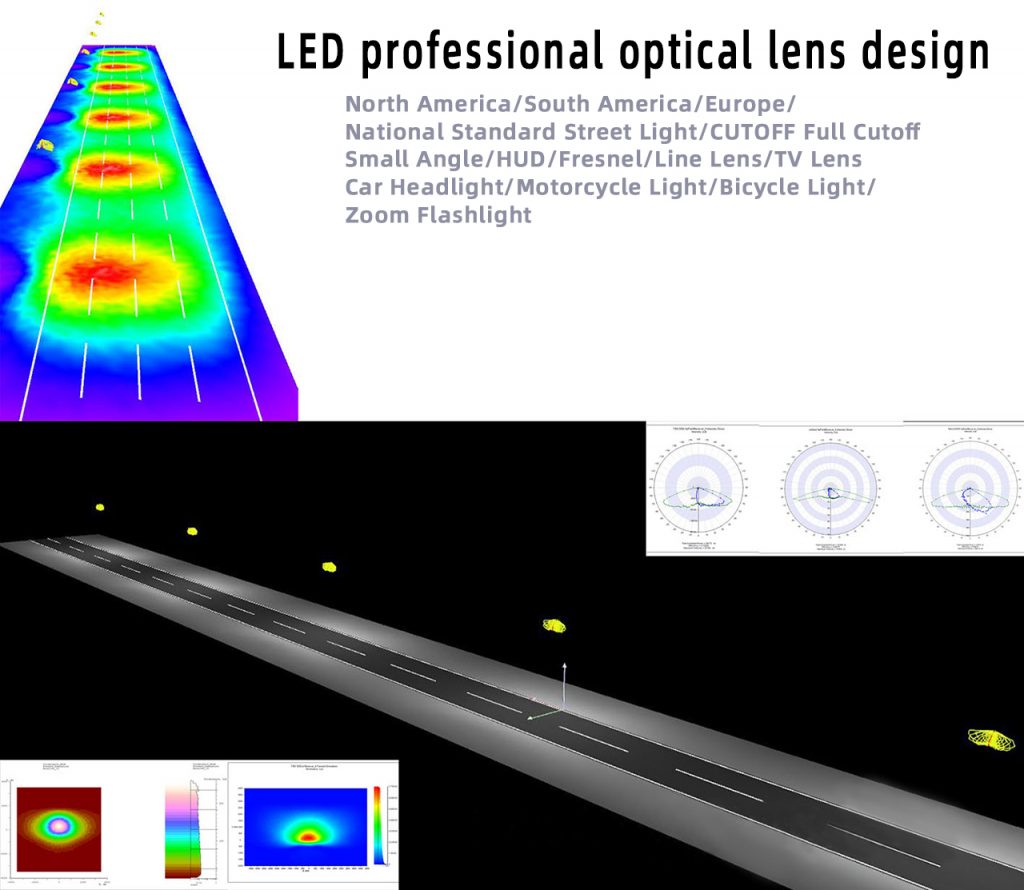
The optical design of glass lenses is a complex process that involves multiple considerations, including optical performance, material selection, manufacturing process, etc. The following are some basic steps and important concepts in the optical design of glass lenses:
1. Clear design goals
Before starting the design, it is necessary to clarify the purpose of the lens, such as:
– Focal length, aperture size
– Aberration control, whether it is necessary to reduce chromatic aberration, coma, etc.
– Application scenarios, such as camera lenses, microscopes, telescopes, etc.
2. Select lens type
Choose the appropriate lens type according to the design requirements:
– Convex lens (positive lens): focusing, used for magnification
– Concave lens (negative lens): astigmatism, used to reduce the image
3. Material selection
Choose the appropriate glass material, different glasses have different refractive index and dispersion characteristics. Commonly used optical glasses include:
– BK7
– Fused Silica
– LaK series, etc.
4. Lens surface design
Design the surface of the lens according to the required focal length and optical properties. Different curvature radii can be used to achieve the desired optical effect. The calculation formula includes:
– The relationship between focal length (f) and radius of curvature (R)
– Similar to the thin lens formula: \( \frac{1}{f} = \frac{(n-1)}{R_1} – \frac{(n-1)}{R_2} \)
5. Aberration analysis
Use optical design software (such as Zemax, Code V, etc.) to perform aberration analysis and optimize the designed lens to minimize aberration and make the image clearer.
6. Combination of optical systems
If multiple lenses are involved, it is necessary to consider lens spacing, optical axis alignment, optical path design, etc., and perform system-level optimization to ensure the performance of the entire optical system.
7. Optical simulation and testing
Use optical simulation tools to perform simulation tests, and adjust and optimize according to the results. Finally, test whether the performance of the actual lens meets the design standards.
8. Manufacturing and post-processing
Cooperate with manufacturers to select appropriate processing methods (such as edge grinding, coating, etc.) to ensure the quality and performance of the lens.
9. Quality Control
After manufacturing, quality control and testing are carried out to ensure that each lens meets the design requirements, such as transmittance, surface quality, etc.
The optical design of glass lenses requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors, including theoretical calculations, material properties, aberration control, etc. Through repeated experiments and optimization, high-performance optical lenses can be designed to meet specific application requirements.

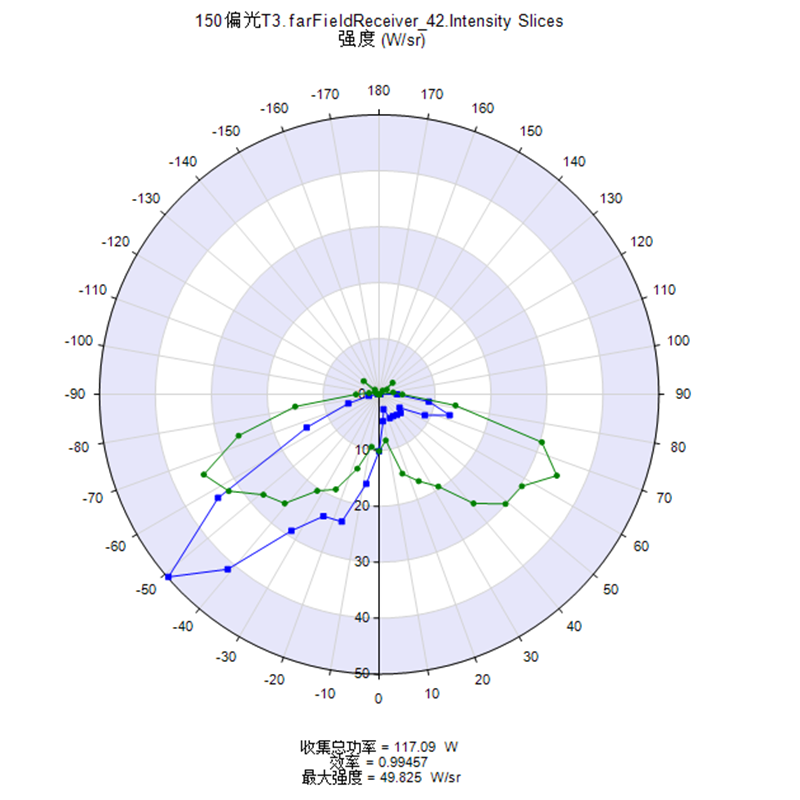
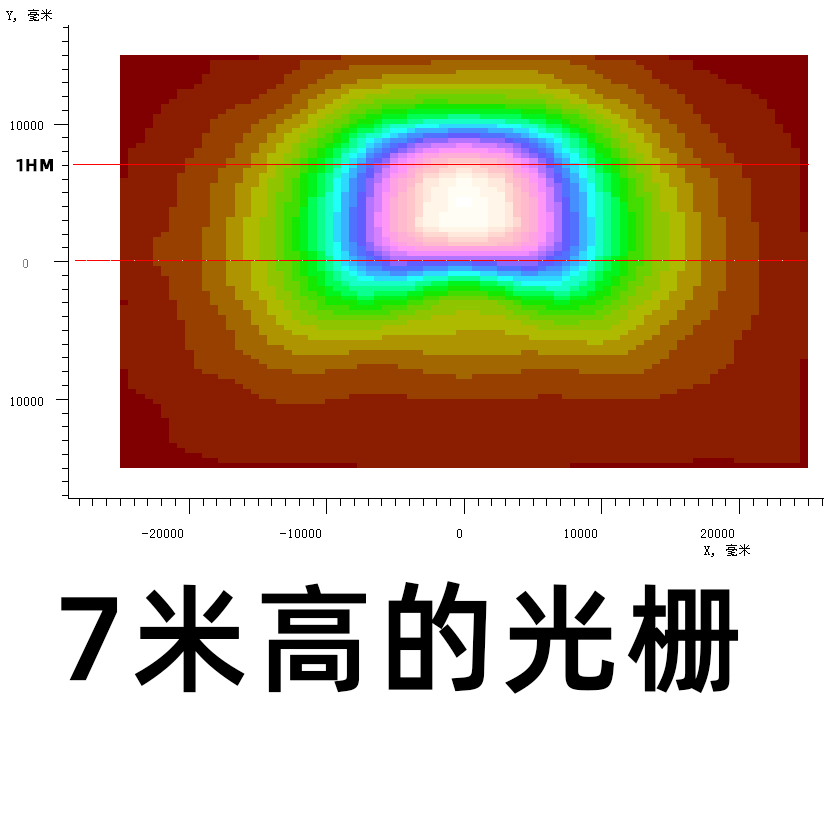


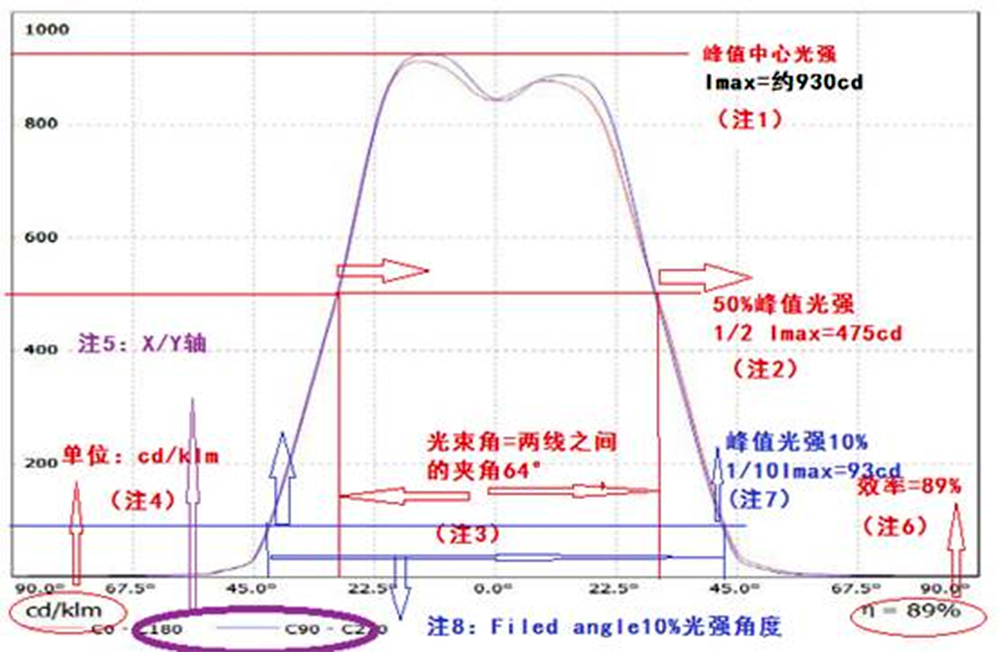

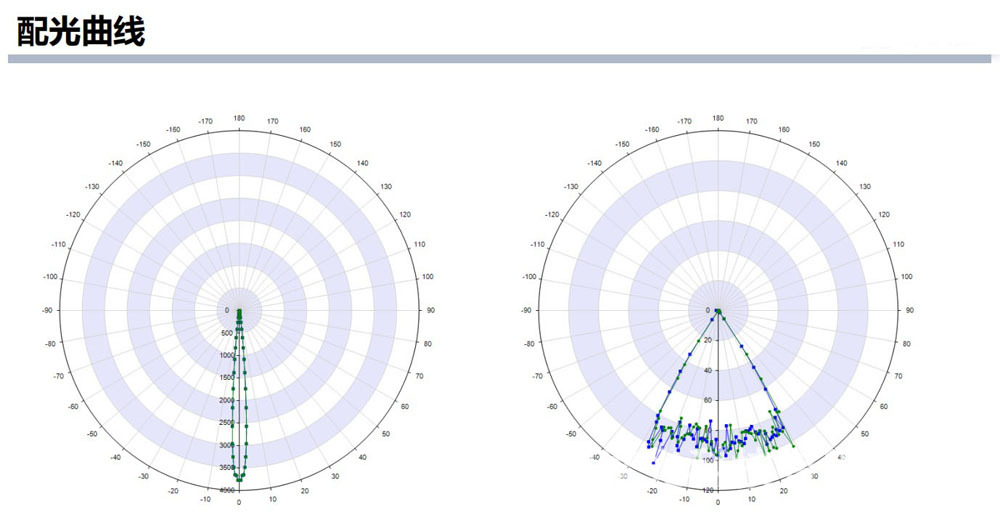
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.